Which Action Would Most Likely Increase The Greenhouse Effect
On this page:
- Overview
- Carbon Dioxide
- Methane
- Nitrous Oxide
- Fluorinated Gases
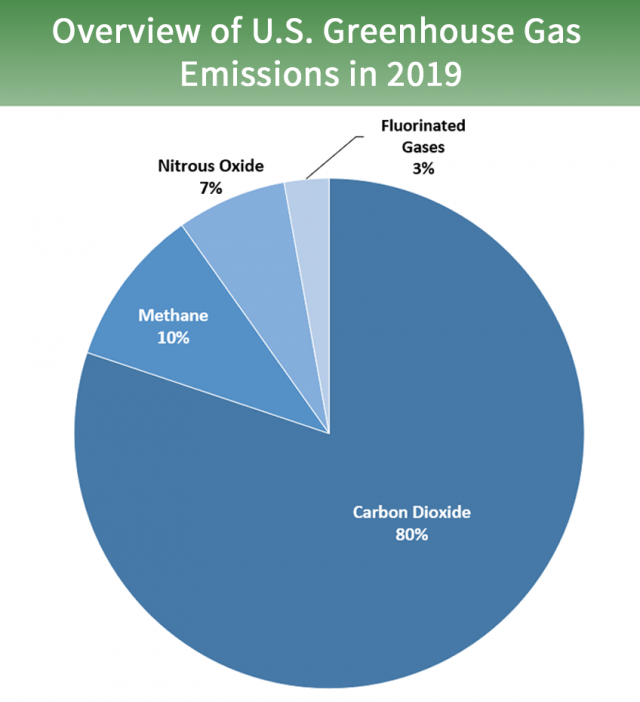
Larger epitome to save or print
Gases that trap oestrus in the temper are chosen greenhouse gases. This section provides information on emissions and removals of the main greenhouse gases to and from the atmosphere. For more information on the other climate forcers, such equally black carbon, please visit the Climate Change Indicators: Climate Forcing page.
- : Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through burning fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil), solid waste product, trees and other biological materials, and also every bit a result of sure chemical reactions (e.thousand., manufacture of cement). Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere (or "sequestered") when it is captivated by plants as function of the biological carbon cycle.
- : Methane is emitted during the production and send of coal, natural gas, and oil. Methane emissions also consequence from livestock and other agricultural practices, state utilise and by the disuse of organic waste in municipal solid waste landfills.
- : Nitrous oxide is emitted during agricultural, land use, industrial activities, combustion of fossil fuels and solid waste, as well as during treatment of wastewater.
- : Hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride, and nitrogen trifluoride are synthetic, powerful greenhouse gases that are emitted from a variety of industrial processes. Fluorinated gases are sometimes used equally substitutes for stratospheric ozone-depleting substances (e.g., chlorofluorocarbons, hydrochlorofluorocarbons, and halons). These gases are typically emitted in smaller quantities, but because they are potent greenhouse gases, they are sometimes referred to every bit High Global Warming Potential gases ("High GWP gases").
Each gas's effect on climate change depends on three master factors:
How much is in the atmosphere?
Concentration, or abundance, is the amount of a detail gas in the air. Larger emissions of greenhouse gases lead to college concentrations in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gas concentrations are measured in parts per million, parts per billion, and even parts per trillion. One role per million is equivalent to one drop of water diluted into nigh 13 gallons of liquid (roughly the fuel tank of a compact car). To learn more about the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, visit the Climate Alter Indicators: Atmospheric Concentrations of Greenhouse Gases page.
How long do they stay in the temper?
Each of these gases can remain in the atmosphere for different amounts of fourth dimension, ranging from a few years to thousands of years. All of these gases remain in the atmosphere long enough to become well mixed, pregnant that the amount that is measured in the atmosphere is roughly the aforementioned all over the world, regardless of the source of the emissions.
How strongly do they impact the atmosphere?
Some gases are more than effective than others at making the planet warmer and "thickening the Earth's blanket."
For each greenhouse gas, a Global Warming Potential (GWP) has been calculated to reflect how long information technology remains in the atmosphere, on boilerplate, and how strongly it absorbs energy. Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy, per pound, than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming World.
Note: All emission estimates are from the Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990–2019.
Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the principal greenhouse gas emitted through homo activities. In 2022, CO2 deemed for about 80 percent of all U.S. greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. Carbon dioxide is naturally nowadays in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon bicycle (the natural apportionment of carbon amid the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals). Human activities are altering the carbon bike–both by adding more CO2 to the atmosphere, and by influencing the ability of natural sinks, similar forests and soils, to remove and store COtwo from the atmosphere. While CO2 emissions come from a diversity of natural sources, man-related emissions are responsible for the increase that has occurred in the atmosphere since the industrial revolution.2

Larger image to relieve or print
The main human activity that emits CO2 is the combustion of fossil fuels (coal, natural gas, and oil) for energy and transportation, although certain industrial processes and land-employ changes also emit CO2. The main sources of CO2 emissions in the United States are described below.
- Transportation. The combustion of fossil fuels such equally gasoline and diesel to transport people and goods was the largest source of CO2 emissions in 2022, accounting for about 35 percent of total U.S. COtwo emissions and 28 percent of total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions. This category includes transportation sources such as highway and passenger vehicles, air travel, marine transportation, and rails.
- Electricity. Electricity is a meaning source of energy in the United States and is used to power homes, business concern, and industry. In 2022, the combustion of fossil fuels to generate electricity was the 2nd largest source of CO2 emissions in the nation, accounting for nigh 31 percent of total U.S. CO2 emissions and 24 percent of full U.South. greenhouse gas emissions. The types of fossil fuel used to generate electricity emit different amounts of COii. To produce a given amount of electricity, burning coal will produce more CO2 than natural gas or oil.
- Industry. Many industrial processes emit CO2 through fossil fuel consumption. Several processes also produce CO2 emissions through chemic reactions that do not involve combustion, and examples include the production of mineral products such as cement, the production of metals such as iron and steel, and the production of chemicals. Fossil fuel combustion from various industrial processes accounted for about 16 percent of total U.Due south. COii emissions and 13 percent of total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions in 2022. Many industrial processes likewise employ electricity and therefore indirectly result in CO2 emissions from electricity generation.
Carbon dioxide is constantly being exchanged among the temper, bounding main, and land surface as it is both produced and absorbed by many microorganisms, plants, and animals. However, emissions and removal of COii by these natural processes tend to remainder, absent-minded anthropogenic impacts. Since the Industrial Revolution began effectually 1750, human activities have contributed substantially to climatic change by adding CO2 and other estrus-trapping gases to the temper.
In the United States, since 1990, the management of forests and other state (eastward.k., cropland, grasslands, etc.) has acted equally a internet sink of CO2, which means that more COtwo is removed from the atmosphere, and stored in plants and trees, than is emitted. This carbon sink beginning is about 12 percent of full emissions in 2022 and is discussed in more detail in the Land Use, Country-Apply Alter, and Forestry department.
To observe out more nigh the office of CO2 in warming the temper and its sources, visit the Climatic change Indicators folio.
Emissions and Trends
Carbon dioxide emissions in the United States increased by about 3 percent between 1990 and 2022. Since the combustion of fossil fuel is the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in the U.s.a., changes in emissions from fossil fuel combustion have historically been the ascendant gene affecting total U.S. emission trends. Changes in COtwo emissions from fossil fuel combustion are influenced past many long-term and curt-term factors, including population growth, economical growth, changing energy prices, new technologies, changing behavior, and seasonal temperatures. Betwixt 1990 and 2022, the increment in CO2 emissions corresponded with increased energy use by an expanding economy and population, including overall growth in emissions from increased need for travel.
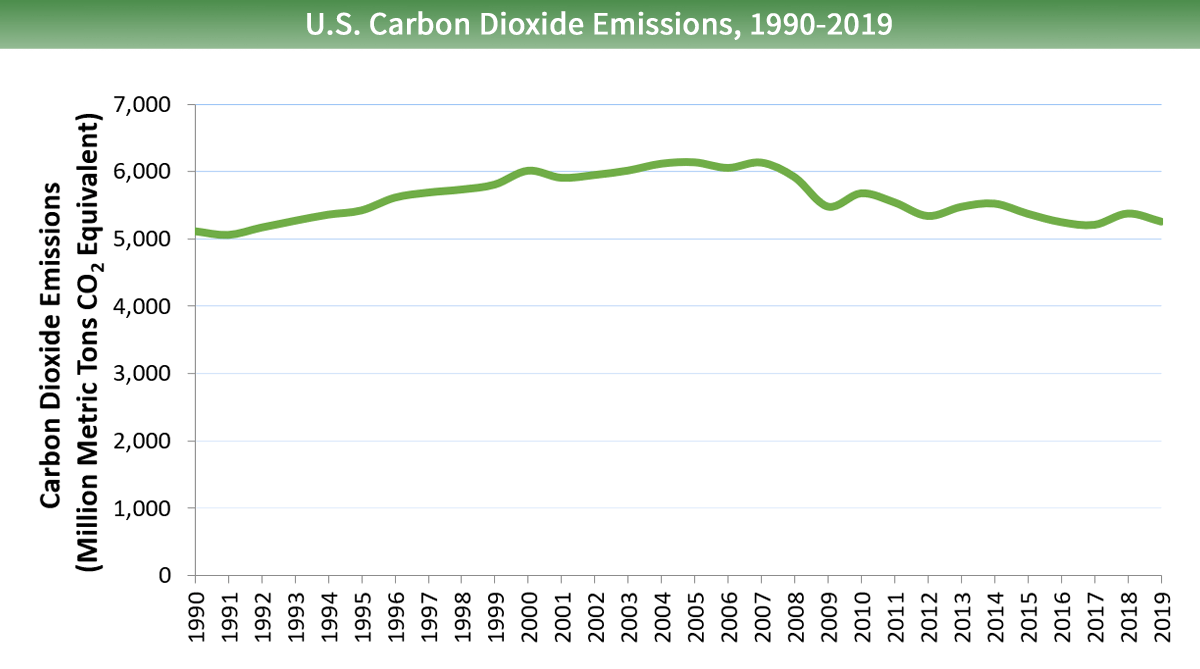
Larger epitome to salvage or impress
Reducing Carbon Dioxide Emissions
The nearly constructive mode to reduce CO2 emissions is to reduce fossil fuel consumption. Many strategies for reducing COii emissions from energy are cantankerous-cut and apply to homes, businesses, industry, and transportation.
EPA is taking common sense regulatory deportment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Larn about EPA's motor vehicle standards.
| Strategy | Examples of How Emissions Can be Reduced |
|---|---|
| Free energy Efficiency | Improving the insulation of buildings, traveling in more fuel-efficient vehicles, and using more efficient electric appliances are all ways to reduce free energy use, and thus CO2 emissions.
|
| Energy Conservation | Reducing personal energy use by turning off lights and electronics when not in use reduces electricity demand. Reducing distance traveled in vehicles reduces petroleum consumption. Both are ways to reduce free energy CO2 emissions through conservation. Acquire more well-nigh What You Tin can Exercise at Home, at Schoolhouse, in the Office, and on the Road to save energy and reduce your carbon footprint. |
| Fuel Switching | Producing more free energy from renewable sources and using fuels with lower carbon contents are ways to reduce carbon emissions. |
| Carbon Capture and Sequestration (CCS) | Carbon dioxide capture and sequestration is a set of technologies that can potentially greatly reduce CO2 emissions from new and existing coal- and gas-fired power plants, industrial processes, and other stationary sources of CO2. For instance, capturing COtwo from the stacks of a coal-fired power plant before it enters the atmosphere, transporting the CO2 via pipeline, and injecting the CO2 deep underground at a advisedly selected and suitable subsurface geologic formation, such as a nearby abandoned oil field, where it is securely stored. Acquire more most CCS. |
| Changes in Uses of Land and Land Management Practices | Learn more virtually Country Use, Land Apply Change and Forestry Sector. |
1 Atmospheric COtwo is role of the global carbon cycle, and therefore its fate is a complex function of geochemical and biological processes. Some of the excess carbon dioxide will be absorbed speedily (for example, by the ocean surface), but some will remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years, due in part to the very boring process past which carbon is transferred to bounding main sediments.
2IPCC (2013). Climatic change 2022: The Concrete Science Ground.Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Cess Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change. [Stocker, T. F., D. Qin, K.-1000. Plattner, M. Tignor, S. M. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P. M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, United states of america, 1585 pp.
Methane Emissions
In 2022, methane (CHfour) deemed for nigh 10 percent of all U.S. greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. Human activities emitting methane include leaks from natural gas systems and the raising of livestock. Methyl hydride is also emitted by natural sources such as natural wetlands. In addition, natural processes in soil and chemical reactions in the atmosphere assist remove CH4 from the temper. Marsh gas'south lifetime in the atmosphere is much shorter than carbon dioxide (COtwo), only CHiv is more efficient at trapping radiations than CO2. Pound for pound, the comparative bear on of CH4 is 25 times greater than CO2 over a 100-yr period.1
Globally, l-65 percent of full CH4 emissions come from human activities.2, 3 Methane is emitted from free energy, industry, agriculture, country utilize, and waste management activities, described below.
- Agriculture. Domestic livestock such as cattle, swine, sheep, and goats produce CH4 as part of their normal digestive process. Likewise, when fauna manure is stored or managed in lagoons or holding tanks, CH4 is produced. Because humans enhance these animals for nutrient and other products, the emissions are considered human being-related. When livestock and manure emissions are combined, the Agriculture sector is the largest source of CHfour emissions in the U.s.. For more information, see the Inventory of U.Due south. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks Agriculture affiliate. While non shown and less significant, emissions of CHfour likewise occur every bit a result of state apply and land management activities in the Land Use, Land-Use Alter, and Forestry sector (e.grand. forest and grassland fires, decomposition of organic affair in coastal wetlands, etc.).
- Free energy and Industry. Natural gas and petroleum systems are the second largest source of CH4 emissions in the U.s.a.. Methane is the primary component of natural gas. Methane is emitted to the atmosphere during the product, processing, storage, manual, and distribution of natural gas and the production, refinement, transportation, and storage of crude oil. Coal mining is likewise a source of CH4 emissions. For more information, see the Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks sections on Natural Gas Systems and Petroleum Systems.
- Waste from Homes and Businesses . Marsh gas is generated in landfills as waste decomposes and in the treatment of wastewater. Landfills are the third-largest source of CHfour emissions in the United states. Marsh gas is also generated from domestic and industrial wastewater treatment and from composting and anaerobic digestion. For more than information, see the Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks Waste chapter.
Methane is also emitted from a number of natural sources. Natural wetlands are the largest source, emitting CH4 from bacteria that decompose organic materials in the absence of oxygen. Smaller sources include termites, oceans, sediments, volcanoes, and wildfires.
To notice out more about the part of CHfour in warming the atmosphere and its sources, visit the Climate Modify Indicators page.
Emissions and Trends
Methane emissions in the United states of america decreased by 15 percentage between 1990 and 2022. During this time period, emissions increased from sources associated with agricultural activities, while emissions decreased from sources associated with landfills, coal mining, and from natural gas and petroleum systems.
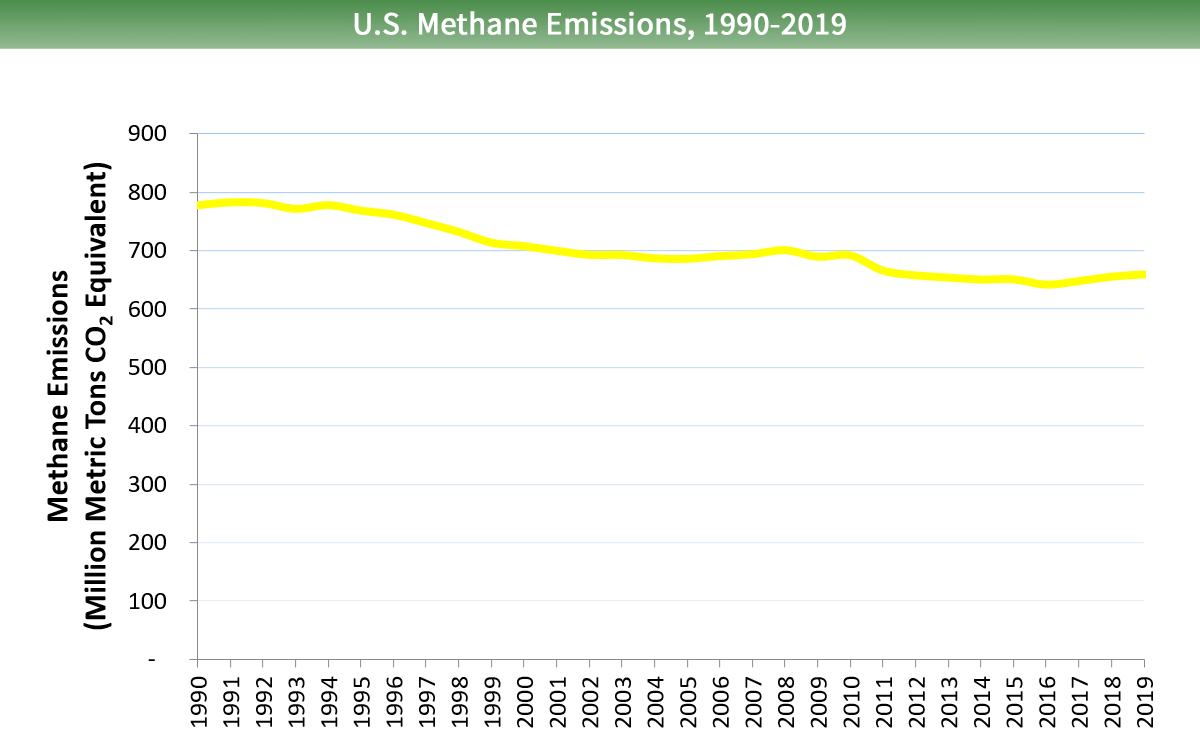
Larger image to save or print
Reducing Methane Emissions
There are a number of means to reduce CH4 emissions. Some examples are discussed below. EPA has a series of voluntary programs for reducing CH4 emissions, in addition to regulatory initiatives. EPA also supports the Global Methane Initiative, an international partnership encouraging global methane reduction strategies.
| Emissions Source | How Emissions Can be Reduced |
|---|---|
| Manufacture | Upgrading the equipment used to produce, store, and send oil and natural gas tin can reduce many of the leaks that contribute to CH4 emissions. Methyl hydride from coal mines can too be captured and used for energy. Learn more than about the EPA'south Natural Gas STAR Plan and Coalbed Marsh gas Outreach Program. |
| Agriculture | Methane from manure management practices tin be reduced and captured past altering manure management strategies. Additionally, modifications to animal feeding practices may reduce emissions from enteric fermentation. Learn more nearly improved manure management practices at EPA's AgSTAR Program. |
| Waste matter from Homes and Businesses | Considering CH4 emissions from landfill gas are a major source of CHfour emissions in the U.s.a., emission controls that capture landfill CH4 are an effective reduction strategy. Learn more about these opportunities and the EPA's Landfill Methane Outreach Program. |
References
aneIPCC (2007). Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change. [S. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, Thousand. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, K. Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, U.k. 996 pp.
2IPCC (2013). Climate Alter 2022: The Physical Science Basis.Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Console on Climate Alter. [Stocker, T. F., D. Qin, G.-Chiliad. Plattner, M. Tignor, S. Grand. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P. K. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.k. and New York, NY, USA, 1585 pp.
iiiThe Global Carbon Project (2019).
Nitrous Oxide Emissions
In 2022, nitrous oxide (N2O) accounted for nigh 7 percentage of all U.S. greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. Man activities such as agriculture, fuel combustion, wastewater management, and industrial processes are increasing the corporeality of NorthwardtwoO in the atmosphere. Nitrous oxide is also naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the World's nitrogen bike, and has a diversity of natural sources. Nitrous oxide molecules stay in the atmosphere for an average of 114 years before being removed by a sink or destroyed through chemical reactions. The touch on of 1 pound of North2O on warming the atmosphere is almost 300 times that of 1 pound of carbon dioxide.1

Larger image to save or print
Globally, about 40 percent of total Due north2O emissions come from human activities.2 Nitrous oxide is emitted from agriculture, land use, transportation, industry, and other activities, described below.
- Agriculture . Nitrous oxide can effect from various agronomical soil management activities, such as application of synthetic and organic fertilizers and other cropping practices, the management of manure, or burning of agricultural residues. Agricultural soil management is the largest source of NtwoO emissions in the United States, bookkeeping for about 75 percent of total U.Due south. NorthiiO emissions in 2022. While not shown and less significant, emissions of Due north2O as well occur as a result of land utilise and land management activities in the Land Apply, Land-Employ Change, and Forestry sector (e.one thousand. woods and grassland fires, application of synthetic nitrogen fertilizers to urban soils (e.thousand., lawns, golf game courses) and forest lands, etc.).
- Fuel Combustion. Nitrous oxide is emitted when fuels are burned. The amount of North2O emitted from called-for fuels depends on the blazon of fuel and combustion technology, maintenance, and operating practices.
- Industry. Nitrous oxide is generated as a byproduct during the product of chemicals such as nitric acid, which is used to make synthetic commercial fertilizer, and in the production of adipic acid, which is used to make fibers, like nylon, and other constructed products.
- Waste. Nitrous oxide is also generated from treatment of domestic wastewater during nitrification and denitrification of the nitrogen present, unremarkably in the grade of urea, ammonia, and proteins.
Nitrous oxide emissions occur naturally through many sources associated with the nitrogen cycle, which is the natural circulation of nitrogen among the atmosphere, plants, animals, and microorganisms that live in soil and water. Nitrogen takes on a diverseness of chemical forms throughout the nitrogen cycle, including NtwoO. Natural emissions of Northward2O are mainly from leaner breaking down nitrogen in soils and the oceans. Nitrous oxide is removed from the atmosphere when it is absorbed by certain types of bacteria or destroyed by ultraviolet radiation or chemical reactions.
To find out more about the sources of NiiO and its part in warming the atmosphere, visit the Climatic change Indicators page.
Emissions and Trends
Nitrous oxide emissions in the United States have remained relatively apartment between 1990 and 2022. Nitrous oxide emissions from mobile combustion decreased by sixty percent from 1990 to 2022 as a outcome of emission control standards for on-road vehicles. Nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural soils have varied during this menstruum and were about 9 pct higher in 2022 than in 1990, primarily driven by increasing utilize of nitrogen fertilizers.
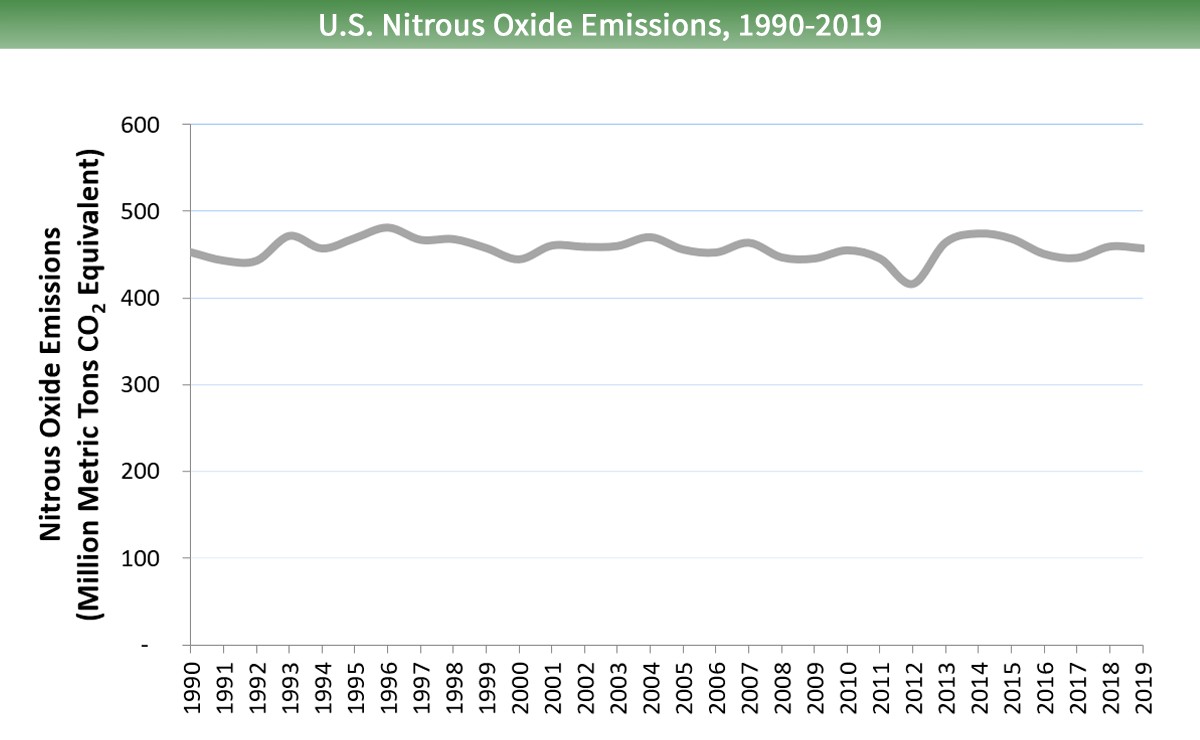
Larger paradigm to save or print
Reducing Nitrous Oxide Emissions
There are a number of ways to reduce emissions of N2O, discussed beneath.
| Emissions Source | Examples of How Emissions Tin be Reduced |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | The application of nitrogen fertilizers accounts for the bulk of N2O emissions in the United States. Emissions tin can exist reduced by reducing nitrogen-based fertilizer applications and applying these fertilizers more efficiently,3 as well equally modifying a subcontract's manure management practices. |
| Fuel Combustion |
|
| Industry |
|
References
1 IPCC (2007) Climatic change 2007: The Physical Science Ground. Contribution of Working Grouping I to the Fourth Assessment Study of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climatic change. [Due south. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, One thousand. Marquis, Grand.B. Averyt, One thousand. Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, United Kingdom 996 pp.
2IPCC (2013). Climate change 2022: The Physical Science Ground. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Cess Written report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. [Stocker, T. F., D. Qin, Grand.-One thousand. Plattner, M. Tignor, Due south. K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, Five. Bex and P. M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge Academy Press, Cambridge, U.k. and New York, NY, USA, 1585 pp.
3EPA (2005). Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Potential in U.S. Forestry and Agriculture. U.S. Ecology Protection Agency, Washington, DC, The states.
Emissions of Fluorinated Gases
Unlike many other greenhouse gases, fluorinated gases have no natural sources and simply come from homo-related activities. They are emitted through their use equally substitutes for ozone-depleting substances (eastward.g., as refrigerants) and through a variety of industrial processes such as aluminum and semiconductor manufacturing. Many fluorinated gases have very high global warming potentials (GWPs) relative to other greenhouse gases, then small-scale atmospheric concentrations tin have disproportionately large furnishings on global temperatures. They tin as well have long atmospheric lifetimes—in some cases, lasting thousands of years. Like other long-lived greenhouse gases, most fluorinated gases are well-mixed in the atmosphere, spreading around the earth after they are emitted. Many fluorinated gases are removed from the temper but when they are destroyed past sunlight in the far upper temper. In general, fluorinated gases are the most potent and longest lasting type of greenhouse gases emitted by human being activities.
There are four main categories of fluorinated gases—hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SFsix), and nitrogen trifluoride (NFthree). The largest sources of fluorinated gas emissions are described beneath.
- Substitution for Ozone-Depleting Substances. Hydrofluorocarbons are used equally refrigerants, droplets propellants, foam bravado agents, solvents, and burn retardants. The major emissions source of these compounds is their use as refrigerants—for example, in ac systems in both vehicles and buildings. These chemicals were adult as a replacement for chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) because they do not deplete the stratospheric ozone layer. Chlorofluorocarbons and HCFCs are beingness phased out under an international agreement, called the Montreal Protocol. HFCs are stiff greenhouse gases with high GWPs, and they are released into the atmosphere during manufacturing processes and through leaks, servicing, and disposal of equipment in which they are used. Newly developed hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) are a subset of HFCs and are characterized past short atmospheric lifetimes and lower GWPs. HFOs are currently being introduced equally refrigerants, droplets propellants and foam blowing agents. The American Innovation and Manufacturing (AIM) Human action of 2022 directs EPA to address HFCs past providing new regime in three master areas: to phase down the production and consumption of listed HFCs in the United States by 85 per centum over the next 15 years, manage these HFCs and their substitutes, and facilitate the transition to next-generation technologies that do not rely on HFCs.
- Industry. Perfluorocarbons are produced as a byproduct of aluminum production and are used in the manufacturing of semiconductors. PFCs generally accept long atmospheric lifetimes and GWPs near 10,000. Sulfur hexafluoride is used in magnesium processing and semiconductor manufacturing, as well as a tracer gas for leak detection. HFC-23 is produced as a byproduct of HCFC-22 production and is used in semiconductor manufacturing.
- Transmission and Distribution of Electricity. Sulfur hexafluoride is used as an insulating gas in electrical manual equipment, including circuit breakers. The GWP of SFhalf-dozen is 22,800, making it the most potent greenhouse gas that the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has evaluated.
To discover out more virtually the role of fluorinated gases in warming the atmosphere and their sources, visit the Fluorinated Greenhouse Gas Emissions folio.
Emissions and Trends
Overall, fluorinated gas emissions in the United States have increased by about 86 pct betwixt 1990 and 2022. This increment has been driven by a 275 pct increase in emissions of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) since 1990, as they accept been widely used as a substitute for ozone-depleting substances. Emissions of perfluorocarbons (PFCs) and sulfur hexafluoride (SFhalf dozen) take actually declined during this time due to emission reduction efforts in the aluminum product industry (PFCs) and the electricity transmission and distribution industry (SFsix).
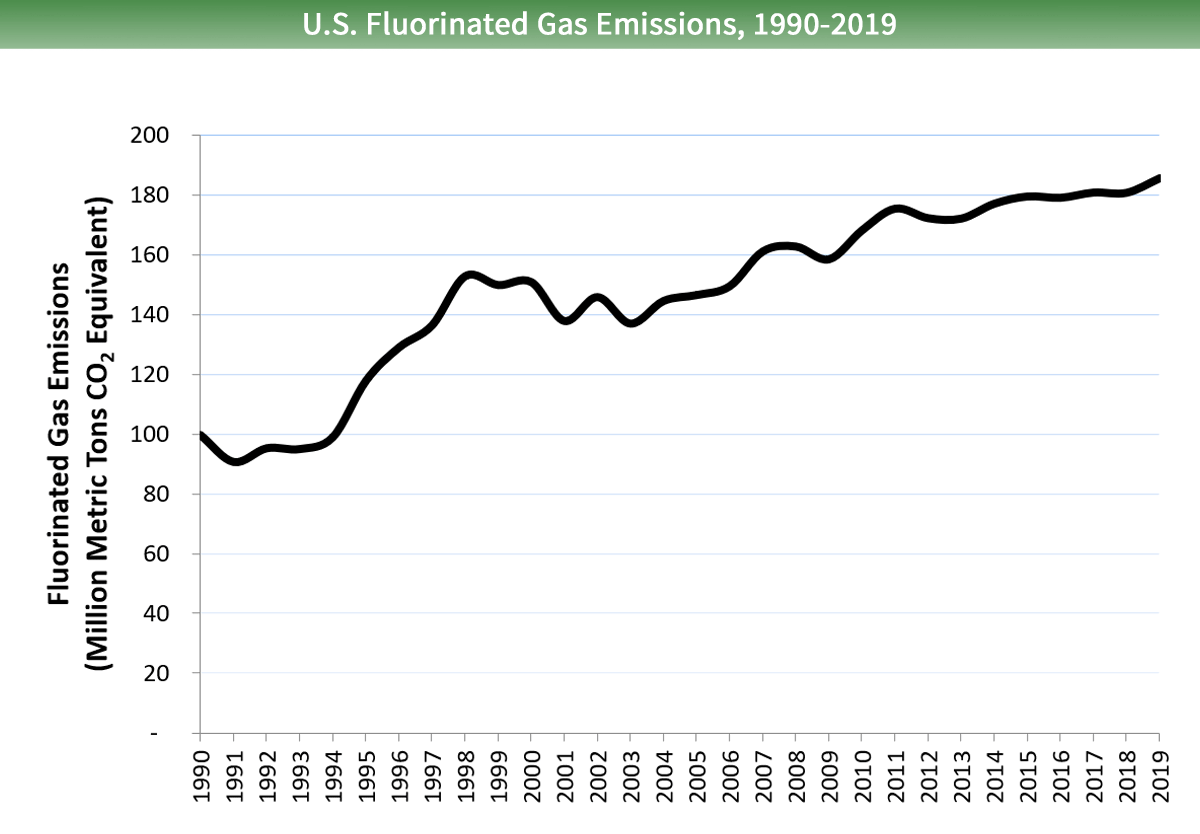
Larger paradigm to save or impress
Reducing Fluorinated Gas Emissions
Considering nigh fluorinated gases have a very long atmospheric lifetime, it will have many years to run across a noticeable reject in electric current concentrations. However, in that location are a number of ways to reduce emissions of fluorinated gases, described below.
| Emissions Source | Examples of How Emissions Can be Reduced |
|---|---|
| Substitution of Ozone-Depleting Substances in Homes and Businesses | Refrigerants used by businesses and residences emit fluorinated gases. Emissions can be reduced by ameliorate handling of these gases and utilise of substitutes with lower global warming potentials and other technological improvements. Visit EPA's Ozone Layer Protection site to larn more about reduction opportunities in this sector. |
| Manufacture | Industrial users of fluorinated gases can reduce emissions by adopting fluorinated gas recycling and devastation processes, optimizing production to minimize emissions, and replacing these gases with alternatives. EPA has experience with these gases in the following sectors:
|
| Electricity Transmission and Distribution | Sulfur hexafluoride is an extremely potent greenhouse gas that is used for several purposes when transmitting electricity through the ability filigree. EPA is working with industry to reduce emissions through the SF6 Emission Reduction Partnership for Electric Power Systems, which promotes leak detection and repair, use of recycling equipment, and employee training. |
| Transportation | Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are released through the leakage of refrigerants used in vehicle air-conditioning systems. Leakage can be reduced through better system components, and through the apply of alternative refrigerants with lower global warming potentials than those presently used. EPA's light-duty and heavy-duty vehicle standards provided incentives for manufacturers to produce vehicles with lower HFC emissions. |
References
aneIPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. [S. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, G.B. Averyt, M. Tignor and H.50. Miller (eds.)]. Cambridge Academy Press. Cambridge, United kingdom of great britain and northern ireland 996 pp.
Which Action Would Most Likely Increase The Greenhouse Effect,
Source: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/overview-greenhouse-gases
Posted by: davismoomple.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Action Would Most Likely Increase The Greenhouse Effect"
Post a Comment